According to Statista, the revenue in the Video Streaming On Demand (SVoD) segment is projected to reach US$24.64bn in 2026. Now when we talk about China, the video content consumption phenomenon in the country has not gone unnoticed. Many companies have set their eyes on this lucrative market. However, the Asian giant has a catch. What works outside China does not necessarily work inside China. With that in mind, in this article, we will explore how to boost your video streaming service in China.
What is a CDN?
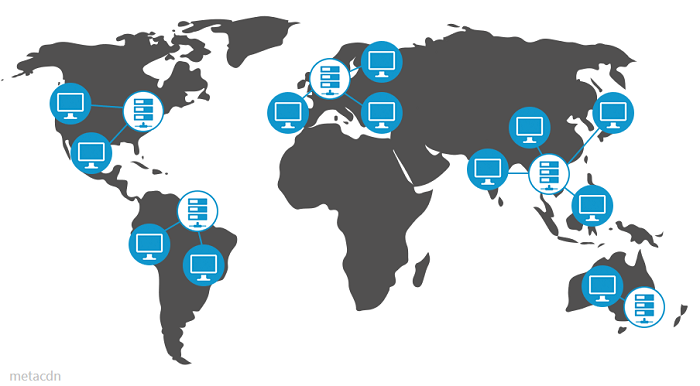
Let's start by reviewing what a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is. You can think of a CDN as a solution to decrease the latency and buffering end-users experience when consuming content, especially multimedia content. To achieve this goal, CDNs use a network of servers distributed at strategic points worldwide. These servers work similarly to Edge Computers because they serve content to the user from the closest node to their location.
While the above explanation is quite simple, it serves the purpose of understanding what a video CDN is. Video CDNs are a particular type of Content Delivery Network explicitly used for streaming video.
Although from one provider to another, there may be differences in the topology, video CDNs are generally based on the following principle:
- ORIGIN SERVER (whether inside or outside China) stores the raw multimedia content
- Audio & video files are uploaded to the transcoding server, which creates several versions optimized for different devices
- Video CDN receives encoded files and replicates them to each CDN node
- The content is served to the user via HLS/HTTP based on the type of device (PC, tablet, phone, etc.)
The best way to illustrate how the video CDN works are through an example. Imagine your origin server is in Europe, and you want to stream video to China. Expect high latency in this scenario due to the distance between your server and users, not to mention the impact of the GFW. On the other hand, a simple topology like the one described above allows you to stream your media files to a server that facilitates consumption on different devices by transcoding the content to optimized formats. From there, the content is distributed to the video CDN, which will serve video or live streaming from the location closest to the user.
Benefits of using CDN for VoD
The previous section briefly discussed some advantages of CDN for streaming video. However, the potential of video CDNs to boost your business goes far beyond what has been discussed.
Latency reduction
When it comes to video streaming, you will notice that one term stands out above the rest, latency. In computer networking, you can think of latency as the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. For example, when not using a CDN, latency would be the time it takes for a data packet to travel from the origin server to the end-user, while when using a CDN, it would be the time it takes for the same packet to travel from the closest node to the user device.
Two factors that have the most impact on latency are the throughput rate of the internet network and the distance between the user and the node serving the content. It is for this reason that CDNs allow a notable decrease in latency since they reduce the distance to the minimum possible.
Load balancing
Using a single origin server to serve content to millions of viewers is a bad idea. A better alternative is to use a CDN since it allows you to distribute the load to different streaming servers. As will be discussed shortly, this also brings benefits from the point of view of scalability, reliability, and high availability. In short, CDNs allow you to spread the load in real-time to optimize video delivery to your audience.
Increased bandwidth and throughput
A direct consequence of the previous point is the improvement of the available bandwidth and throughput. In the context of streaming video, it is common to confuse bandwidth with latency. One way to understand these concepts is by visualizing a highway. Bandwidth is the amount of data you are transmitting, or put another way, the number of cars on the highway at any given time. Bandwidth is generally measured in megabits per second, while latency is measured in milliseconds.
When you distribute the streaming load between different nodes, you are somehow opening more channels on the highway, which minimizes the possibility of congestion and allows you to maximize resources.
The difference in latency with and without a CDN?
To show the difference in latency between using a CDN and not, we will use the most common case as an example: video on demand. When streaming video, latency is the delay in milliseconds that the user perceives when interacting with the VoD service. This latency can manifest itself in different ways depending on its magnitude. The user could experience anything from minor lags to uncomfortable waiting periods while the device buffers the content.
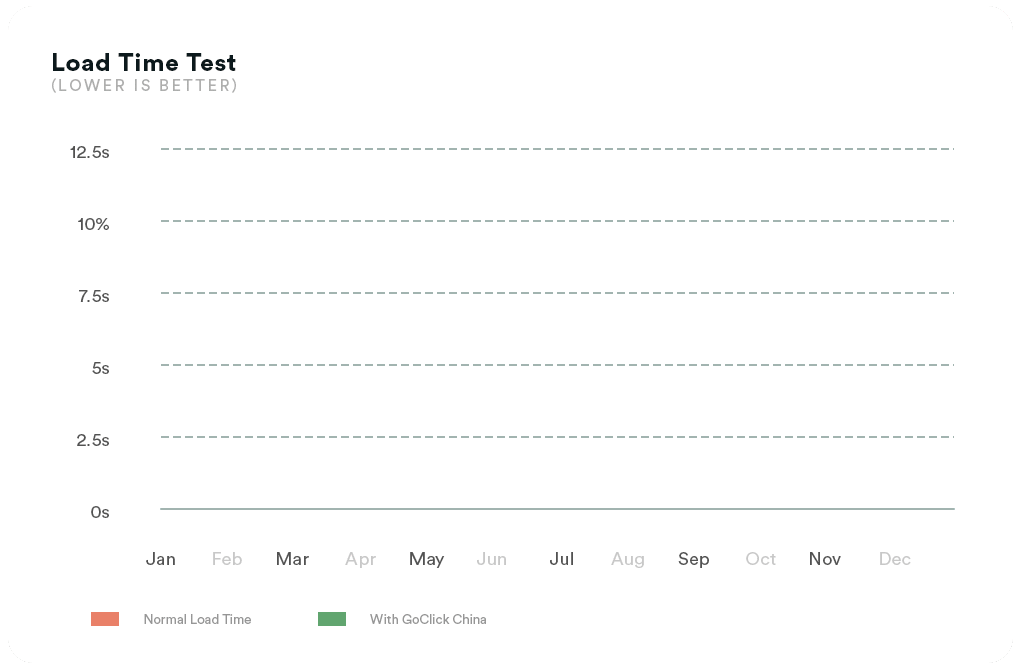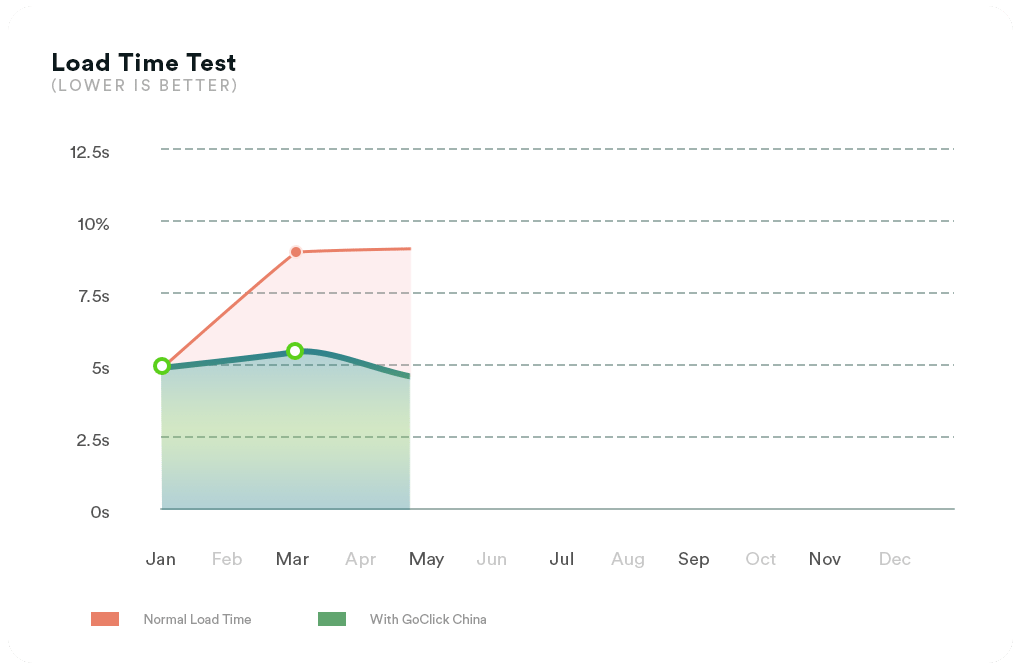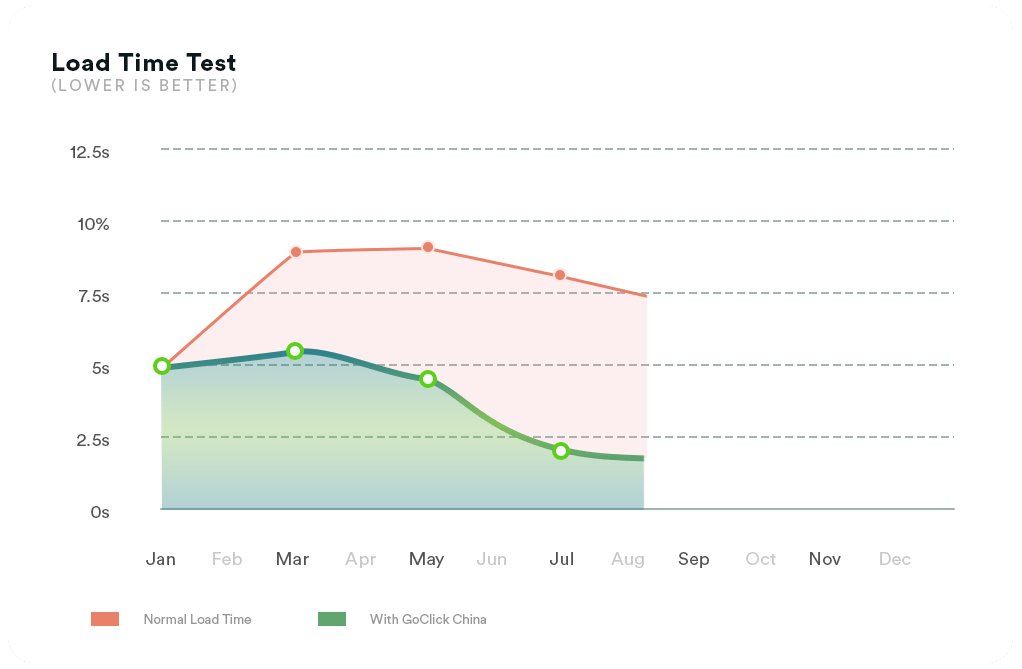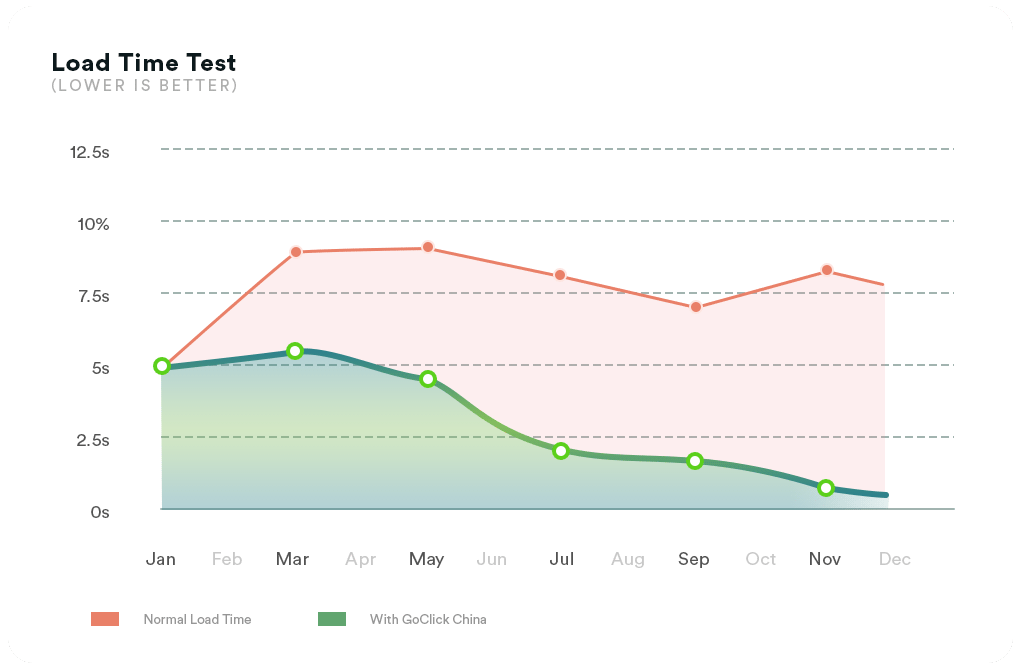
Without video CDN. Depending on the distance to the user, hardware encoders, percentage of packet loss, and network speed, the latency could be as high as 5-20 seconds or even more.
With video CDN. Using a CDN service optimized for streaming video, viewers could experience low latency between 1 to 5 seconds or even ultra-low latency of less than a second.
In practice, the goal of most video CDN providers is to offer users a latency under 100 milliseconds (one-tenth of a second), even during peak hours. However, you can expect latency to be as low as 1-15 ms under normal circumstances. This ultra-low latency is practically imperceptible to the human eye.
Why is CDN necessary for streaming video on demand?
If anything is clear from the previous section, it is that high latency kills the viewing experience. When it comes to video latency, every millisecond counts, it is for this reason that if your business wants to venture into the booming VoD market in China, a video CDN is a must. But don't take our word for it; see for yourself why your organization needs a CDN for streaming video.
- Scalability: scaling without a CDN is almost impossible. As the number of viewers spikes up, you need an infrastructure that can handle the increased demand in real-time. Video CDNs are meant for these scenarios, where a larger number of nodes can be added during peak hours or special events.
- Quality: the user experience is not only determined by latency but also by the quality of the video they enjoy. In this sense, CDNs are prepared to serve optimized content according to the device that requests it. Thus, video CDNs encode streaming in multiple formats that allow optimization of bandwidth and quality in real-time.
- Reliability: one of the most exciting features of video CDNs is their built-in failover capability. If one node or virtual machine fails, another one wakes up and takes its place. This ensures that your audience will experience smooth content with minimal interruptions or buffering issues.
- Enhanced Performance: Most video CDN providers make sure to offer a comprehensive solution that is responsible not only for distributing the content but also for optimizing the entire transmission process (transcoding, adaptive bitrate, video caching, enhanced bandwidth, etc.). For this reason, it is not surprising that streaming video with a CDN is noticeably more efficient and faster than without it.
- Increased Availability: In addition to having failover mechanisms, a strategy that can increase the availability of your service is to use multiple CDNs to serve the content. To delve into the exciting topic of multi-CDNs, we suggest you read this article on our blog.
- High Security: when streaming video, security is crucial. For that reason, to prevent fraud and other types of risks during video transmission, most CDNs have AES encryption, secure data centers, anti-phishing protection, and other security mechanisms.
- Reduced abandonment and increased conversions: VoD viewers' expectations are higher than ever. If during the first few seconds of streaming, users experience high latency, low video quality, excessive buffering, or other issues, they will quit steaming without a second thought. Worse yet, regaining the trust of said users is no easy task. This is possibly the strongest argument for using CDNs, minimizing abandonment, and guaranteeing conversions. If you still need another argument, then just watch what the competition is doing. Does your competition use a video CDN? Most likely, the answer is yes. After reading all the advantages of using a CDN, do you really think that it is a good idea for your competition to take the lead?
To delve deeper into multi-CDN solutions, we suggest our article Multi-CDN: a solution for CDN outages.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, the importance and benefits of video CDNs have been explained. By now, you should have a clearer idea of why CDNs are crucial to ensuring the best possible user experience. This begs the question, which CDN should you use? Is it better to use a single CDN, or is it more profitable to implement a multi-CDN strategy?
The answer is that it depends. As we mentioned in the introduction, the Chinese market is unique. The presence of the GFW makes it crucial to rely on experts who can advise your business on which solution best suits your needs. At GoClick China, we offer you both single CDN and multi-CDN professional services, as well as advice on how to boost your streaming service in China. Our solution consists of a custom API that assists you in selecting the best CDN at any given time, which gives you greater resilience against service outages. Contact one of our specialists today for more detailed information about our services.



