What are DNS and Anycast?
What’s DNS? A domain name system (DNS) is like a phone book for the internet, it turns www websites into IP addresses that devices can read.
The DNS service is necessary for the internet world because every internet node communicates by IP address, but IP addresses are too difficult for a human to read and remember. So DNS service will convert human-readable domain names to the IP address. For example, the service maps addresses (e.g. 157.240.3.35) to a domain name (e.g. facebook.com), which is much easier for humans to remember.
With DNS service, internet users can just type the domain name in the browser, and the DNS service will transform it to the correct IP address, then the browser will be able to talk to the target server according to the IP address. The user then can get the content from the server or post data to the server as needed.
What’s Anycast? Anycast is a one-to-one-of-many routing scheme where the same IP address is assigned to multiple servers. The methodology routes website packets to a single member of a group of potential receivers with the same IP.
Packets sent from the host to an Anycast IP will reach different servers (or nodes) to distribute the load and reduce latency. If a node or server goes offline, the router will no longer send to that server and send to the nearest one, according to its normal decision-making algorithms. The routing algorithm selects the single receiver from the group based on the least-expensive routing metric.
User requests are directed to specific nodes based on factors such as capacity and the health of your server, as well as the distance between it and the website visitor. In short, Anycast is one source that can talk to a service that is hosted on multiple nodes configured with the same IP address.
What is DNS Anycast?
DNS Anycast technology automatically routes DNS queries to the closest geographical available server. If there’s a regional failure, the DNS resolution request will be rerouted around and go to the next closest DNS server. With this mechanism, the reliability of DNS service gets increased. The DNS lookup latency will be reduced as much as possible because the query will always be sent to the nearest node. The probability of being attacked by DDOS is also reduced significantly since the failed nodes will be removed from the group automatically and the request will be rerouted to the available ones. As long as there are some nodes in the group that still work, the DNS service will still work.
Any server that becomes unavailable due to failure or routine maintenance will have a very limited impact on the DNS server because the failed server can be removed from the routing tables. Routing will divert the traffic to the new alternative servers in the Anycast group.
What is the advantage of Anycast?
There are several advantages to Anycast routing, including:
- Faster connections – a DNS query will go to a network of DNS resolvers rather than to one specific resolver, and it will be routed to whichever resolver is closest and available. DNS queries and responses will follow optimized paths in order to answer queries as quickly as possible. It thus minimizes round-trip time (RTT), thereby decreasing the number of hops and reducing latency.
- Simplified server configuration – You have just one IP that is assigned to every server, no matter where they are in the world. In more traditional DNS solutions, you would have to configure for every location separately. Anycast lets a single DNS server configuration distribute to all of your network nodes.
- High availability – Advertising an IP address on multiple nodes creates redundancy, thereby providing backup in the event that any node becomes overloaded or fails.
- DDoS mitigation – Anycast provides intrinsic DDoS mitigation by offering failover alternatives if a node is attacked or goes down.
- Load balancing - Using layer three dynamic Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing protocol, Anycast IP addresses will effectively load balance DNS queries over different nodes based on geography. If equal- cost route paths are visible from one geography, all nodes can be used.
How Anycast works in China
The internet in China is totally different from the global internet. Actually, China's internet is almost like a country-wide intranet, like an island that has limited entry/exit points. The Great Firewall censors the content that is transferred between inside and outside China. The technologies that the GFW used include limiting access to foreign information sources, blocking foreign internet websites (Google, Facebook, Twitter, Wikipedia, and others) and mobile apps, and requiring foreign companies to adapt to China's domestic regulations.
As a result of this policy, multinational companies like Cloudflare can deploy freely anywhere but China. There are, however, server providers such as Xirsys that have established partnership with Chinese companies that have data centers within China.
In China, there are three major internet service providers (ISPs), China Telecom, China Unicom and China mobile, each with its own DNS and Anycast network. These ISPs don't speak directly to each other for lack of peer-to-peer connections. Because of the competition among them, they purposely limit the bandwidth and performance of their interconnections.
Then there are those big internet companies such as Baidu, Tencent and Alibaba that also offer DNS services with Anycast. Alibaba, for instance, every year, holds the country's largest online shopping event, Singles Day (Double 11 shopping festival). On this day there are billions of visits to the website and Alibaba must make sure that the load to every server works, and that the load is balanced to make sure no website drops a shopper on the site.
The Anycast IP addresses from the Chinese DNS/CDN providers broadcast vertically to the nodes along the backbones of the 3 ISPs rather than to the entire internet. In such a way, if the client and the server are both using the same ISP, the performance is good. But if either one is using another ISP, the performance will be unreliable. Because of the poor interconnection among their backbones, horizontal broadcast to competitor’s networks will entail huge delays, defeating the purpose of using the Anycast technology in the first place. In the search for the logically shortest equal-cost paths, they may even route traffic physically to overseas networks. This routing strategy results in traffic misalignment that further complicates the landscape and leads to even greater latency. The poor performance can be expected due to the nature of the overseas connection quality and bandwidth. This is totally diverted from the purpose of anycast.
Because of the above situation, it’s not easy for everyone to benefit from Anycast in China’s internet.
Does DNS Anycast work in China?
The short answer is yes. But it’s not the same as it works outside China. As described previously, the customer won’t be able to benefit from Anycast in China without an extra setup. Alibaba deploys its own DNS Anycast servers. However, they all broadcast individually within each operator, rather than from one operator to other operators. The reason is the inter-operator access is purposely limited. The competition of the wideband market among the operators is fierce because the market is reaching saturation. The operators would purposely decrease the user experience when accessing the network to other operators so that the user’s perception of the other operators would be negative. They would most likely stay with the current ISP they’re using and not switch to others.
For example, Beijing Telecom wants to do a broadcast across all three networks from the ISPs, then the as-path of a Shanghai Mobile user to access this Anycast would probably be like this: Shanghai Mobile → China Mobile backbone → China Telecom backbone → Beijing Telecom. Because of the reason mentioned above, the connection between the China Mobile backbone and China Telecom backbone has poor performance. Normally there is huge latency between those two nodes. So the Anycast deployed in this way won’t work well for the users.
Another possible reason for the slow as-path cross-network penetration broadcast is that, in their BGP path selection, the operators may choose an overseas as-path, which is logically shorter than a domestic route in this scenario, resulting in traffic misalignment. And because of the physical long route of the overseas as-path, the performance and the reliability would be degraded.
The key to resolving the problem is to avoid the interconnection between the backbone connection between different ISPs. If the broadcast is done internally within the three networks separately, and change the above as-path to Shanghai Mobile → China Mobile → Beijing Mobile or Shanghai Telecom → China Telecom → Beijing Telecom, this setup will get much less latency because the route gets around the poor interconnection between the ISPs. With this improvement, the DNS resolution time will be reduced significantly, the user will experience better performance than before.
To illustrate the loading speed between a China DNS and a non China DNS, we conducted a synthetic loading speed test in different hosting scenarios. In this test, loading speed appears faster with the China DNS than with a non-China DNS in different hosting scenarios. We tested the same website at the same time of day, using the same devices, the only difference is hosting the DNS in China or outside of China.
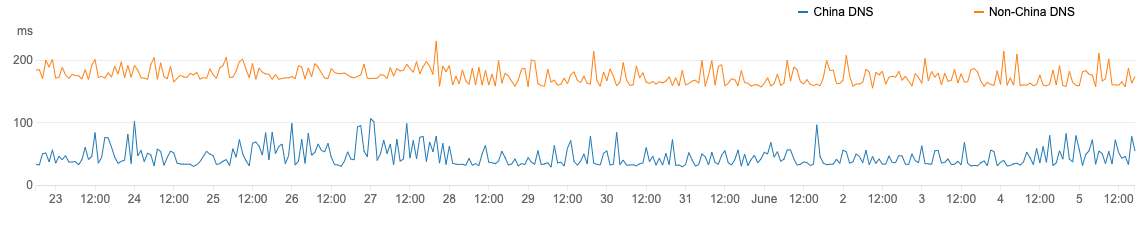
From our testing services, you can tell the loading time difference from the chart above, and from the below video, it’s not just the loading time that is 10 times diff, but also the non-China DNS has come to a broken image at the end.
Here’s a webpage loading speed comparison test which is conducted in different DNS hosting scenarios.
How is this relevant to your website in China?
If your target market is in China and your potential customers are in China, while you host your website outside China, your website could be blocked by the Chinese government because of the internet regulation.
The technology used to block the sites vary, so your website could also experience different kinds of issues. Your customer could experience a slow loading speed, incomplete web page loading, or even fail to connect to your site completely. Among these issues, DNS in China is one of the most critical issues that you need to address. The default DNS servers which are provided by the Chinese ISP could return a DNS resolution failure message or spoofed IP address when your customer submits a DNS request. A failed DNS resolution result will make your site totally inaccessible. Your customers will believe your service is not ready yet. This can pose a challenge for your business in China.
To be more specific, let’s say your website is www.new-website.com and the actual IP is aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd. When your customers in China try to visit your application via this URL, they may fail in several different ways. They may not get the IP address at all, the DNS server that ISP used could just return a DNS lookup failure and your customer could just see an HTTP network error code in their browser. They don’t know what happened so they may guess that your website is down. Or they might receive a correct IP address long after the DNS request is submitted. In this case, your website will finally be loaded but maybe just partially because some components of your web page loading time has expired. In the worst case, they might even receive a fake IP address that is different from your actual IP address aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd. The fake IP address will bring them to other sites. In all the cases, visitors have a low chance of getting to your application successfully.
Most likely your customers will leave your application and turn to other alternatives available in China, maybe your Chinese competitors. However, this doesn’t mean it is impossible to get around the issue. Anycast DNS is still a practical, sophisticated technical solution that can help visitors get the right DNS resolution, but you just need to know more about how to use it in China.
Next steps
To better understand where you can improve your services, a synthetic testing solution will continuously simulate users to visit the DNS servers from all over China and collect a set of KPIs which is useful to monitor the DNS servers’ status. In this way, the DNS issue in China can be addressed. GoClick China provides the clients an easy way to build their business in Mainland China.
To learn more about succeeding in China, check out our other articles.



